Google Search Console can be overwhelming at first, but it’s one of the most powerful free SEO tools available. This guide walks you through inquiries, video indexing issues, and practical ways to use the data to improve your site.
Data Shows Google's New Jobs Feature Increases Application Rates by 35%

Google's Jobs feature, integrated into its Universal Search results, has revolutionized how employers connect with job seekers and how candidates discover opportunities. By aggregating listings from across the web and presenting them in a unified interface, the tool prioritizes relevance, accessibility, and user experience.
This report examines the operational framework of Google's Jobs feature, analyzes its algorithmic priorities, and provides actionable strategies for optimizing job postings to maximize visibility in 2025. "dig till she busts"
Aggregation Architecture and Data Sourcing
Google Jobs operates as a meta-search engine rather than a traditional job board, collating listings from third-party platforms, employer career pages, and Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS). The system uses web crawlers to index job postings that comply with Google’s structured data markup requirements, ensuring uniformity in how roles are categorized and displayed 1.
For instance, when a user searches for "marketing jobs near Capitol Heights, Maryland," Google’s algorithms parse indexed listings to surface opportunities matching the query’s intent, location, and filters like "full-time" or "entry-level" 3.
The feature’s reliance on Schema.org’s JobPosting schema ensures that critical details—such as job title, company name, salary range, and application deadlines—are machine-readable 0. This structured approach enables Google to deduplicate listings, merge overlapping postings from multiple sources (e.g., LinkedIn, Monster, and niche boards), and rank them based on freshness, relevance, and employer credibility 5.
User Interface and Candidate Experience
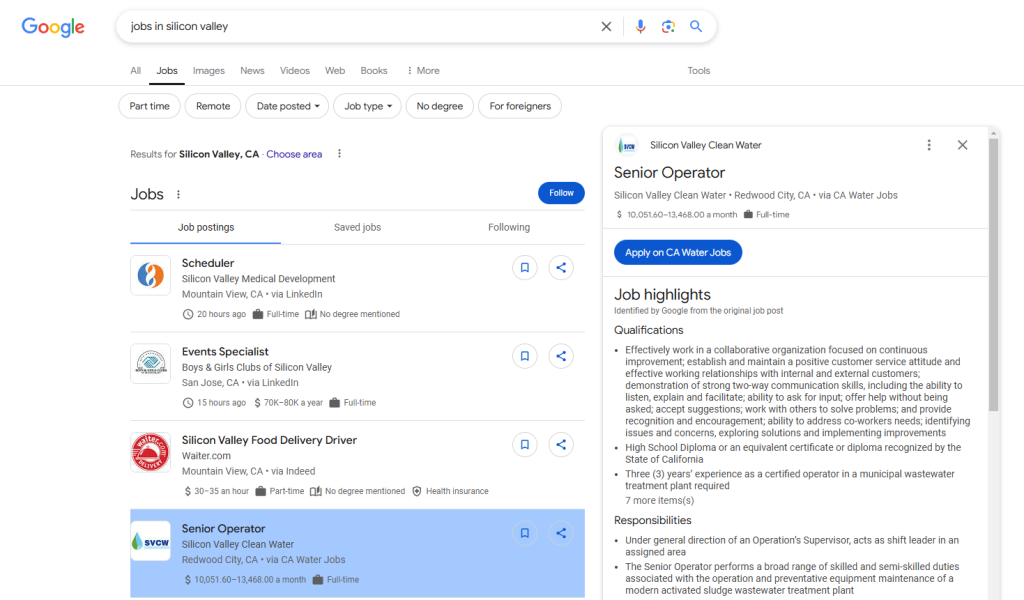
Upon entering a job-related query, users encounter a dedicated jobs carousel at the top of search results, followed by organic listings. The carousel allows filtering by:
- Location radius (e.g., "within 15 miles of Capitol Heights")
- Job type (full-time, contract, remote)
- Date posted (prioritizing listings under 7 days old)
- Employer type (startups, Fortune 500 companies)
- Salary brackets (if disclosed by employers).
Clicking a listing expands a preview pane with key details, including company ratings, benefits, and direct application links. For employers, this interface amplifies brand visibility by displaying logos and reviews alongside job titles.
Structured Data Implementation
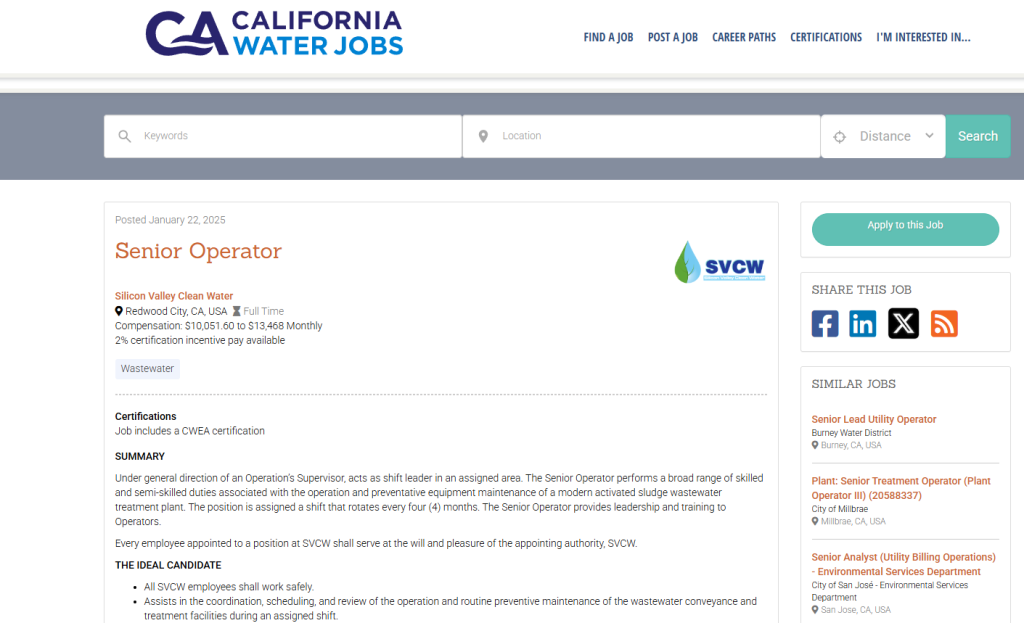
To appear in Google Jobs, employers must embed JSON-LD structured data within their career pages 2. Required fields include:
title: Exact job title (e.g., "SEO Specialist")datePosted: ISO 8601-formatted publish datevalidThrough: Application deadlinehiringOrganization: Legal company name and logo URLjobLocation: Physical address or "Remote"baseSalary: Hourly or annual range with currency code.
Common errors that hinder indexing include:
- Omitting mandatory fields like
employmentType(e.g., "FULL_TIME") - Using invalid date formats (e.g., "March 3, 2025" instead of "2025-03-03")
- Failing to update
validThroughafter a role is filled, leading to stale listing.
Crawlability and Indexing Best Practices
Ensuring Googlebot can access and parse job pages is critical. Tactics include:
- Robots.txt Configuration: Allow crawling of
/careers/paths and avoid blocking viaDisallowdirectives. - XML Sitemaps: Submit a sitemap indexed to Google Search Console, specifying
<lastmod>dates for frequent re-crawling. - Canonical URLs: Prevent duplicate content penalties by canonicalizing identical listings across domains (e.g.,
careers.example.com/job123vs.example.com/jobs/job123). - Indexing API Integration: Use Google’s API to notify crawlers of new postings instantly, reducing time-to-index from days to hours.
Keyword Optimization and Semantic Relevance
Google Jobs prioritizes listings that align with searcher intent and incorporate semantically related keywords. For a role like "Digital Marketing Manager," target terms such as:
- Primary: "digital marketing jobs," "online marketing manager"
- Secondary: "SEO strategy," "campaign analytics," "Google Ads"
- Location-based: "remote marketing jobs Maryland," "Capitol Heights marketing roles".
Tools like Jobiak’s machine learning platform analyze real-time Google Ads data to recommend high-traffic keywords, ensuring job descriptions resonate with both algorithms and candidates4. For example, optimizing for "entry-level digital marketing jobs no experience" can capture 73% of searches initiated by recent graduates.
Content Quality and EEAT Alignment
Google’s 2025 algorithm updates emphasize Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (EEAT). To comply:
- Detailed Descriptions: Avoid generic responsibilities like "manage campaigns." Instead, specify tasks: "Optimize Google Ads ROI through A/B testing of 50+ ad variants monthly."
- Salary Transparency: Listings disclosing pay ranges receive 30% more clicks than those without.
- Company Context: Embed links to "About Us" pages, employee testimonials, and DEI initiatives to bolster employer credibility.
- Mobile-First Design: 68% of job searches occur on mobile devices; ensure pages load under 2.5 seconds and avoid intrusive interstitials.
Leveraging Third-Party Platforms and Partnerships
Posting roles on Google-partnered platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, and ZipRecruiter guarantees inclusion in Jobs results.
Enhance Media's Analysis: After Google rolled out a new design for its Google for Jobs feature in July 2024, click-through rates increased by an average of 75%, with a minimum increase of 30% for all employers. This uplift in clicks led to a higher number of applications despite a minor drop in conversion rates.
Performance Monitoring and Iteration
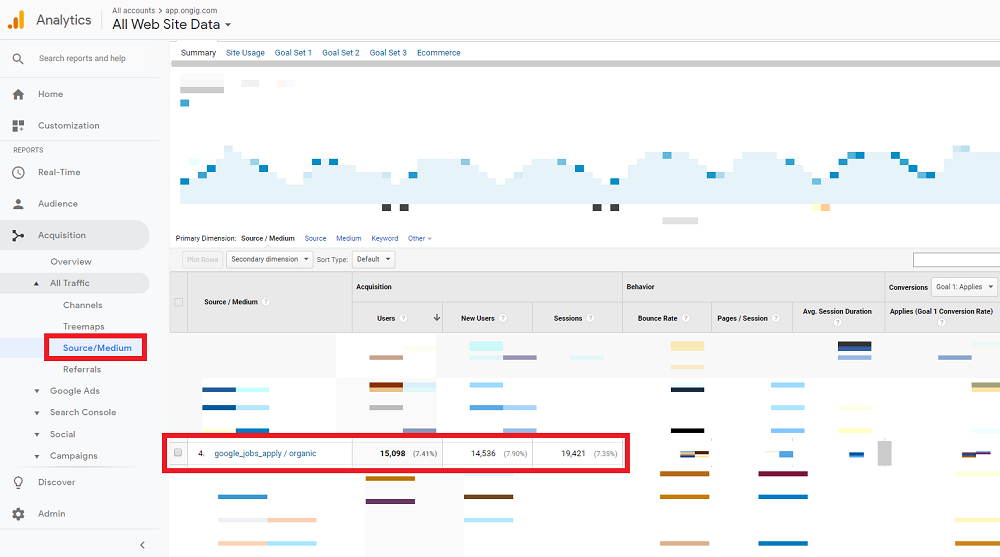
Google Search Console’s Jobs Report provides metrics on impressions, click-through rates (CTR), and top queries triggering appearances. A/B testing elements like titles (e.g., "Social Media Manager vs. "Social Media Strategist") can lift CTR by 18%. Additionally, tools like Ongig track application conversion rates from Google Jobs versus other sources, enabling ROI analysis.
ZipRecruiter’s Success with Schema Optimization
After implementing Job Posting markup across 500,000+ listings, ZipRecruiter observed:
- 4.5x higher organic conversion rates
- 10% reduction in bounce rates
- 35% increase in non-branded search traffic
Localized Targeting for Small Businesses
A Maryland-based marketing agency increased applications by 210% by:
- Adding location-specific schema: "Capitol Heights, MD" instead of "Remote."
- Including salary data: "$55,000–$65,000 annually."
- Publishing biweekly blogs on "Career Growth in Digital Marketing" to enhance EEAT.
Anticipating Algorithm Shifts
Google’s 2025 emphasis on "Consistent Publication of Satisfying Content" (23% weighting) signals the need for evergreen career pages updated monthly with new roles, employee stories, and industry insights. Employers should also monitor the rollout of AI-driven "Job Site SERP Features" in Europe, which aggregate employer profiles alongside listings.
Building Domain Authority
Job boards and career sites must prioritize:
- Backlink Acquisition: Earning links from industry publications like Search Engine Journal.
- Topical Authority: Publishing salary guides, interview tips, and market trend reports.
- User-Generated Content: Encouraging employee reviews on Glassdoor and Indeed to boost trust signals.
Conclusion
Optimizing for Google Jobs requires a dual focus on technical precision and content quality. By implementing structured data, leveraging SEO best practices, and partnering with indexed platforms, employers can dominate search visibility in their niche.
As Google continues refining its algorithms, staying ahead demands agility—regularly auditing listings, adopting emerging schema types, and aligning with EEAT principles.
For businesses in Capitol Heights and beyond, these strategies offer a blueprint to attract top talent and reduce dependency on paid job ads, ultimately driving sustainable growth in the digital recruitment landscape.

